Companion@360 → 7 Month programme to sharpen your writing skills → REGISTER NOW
Introduction
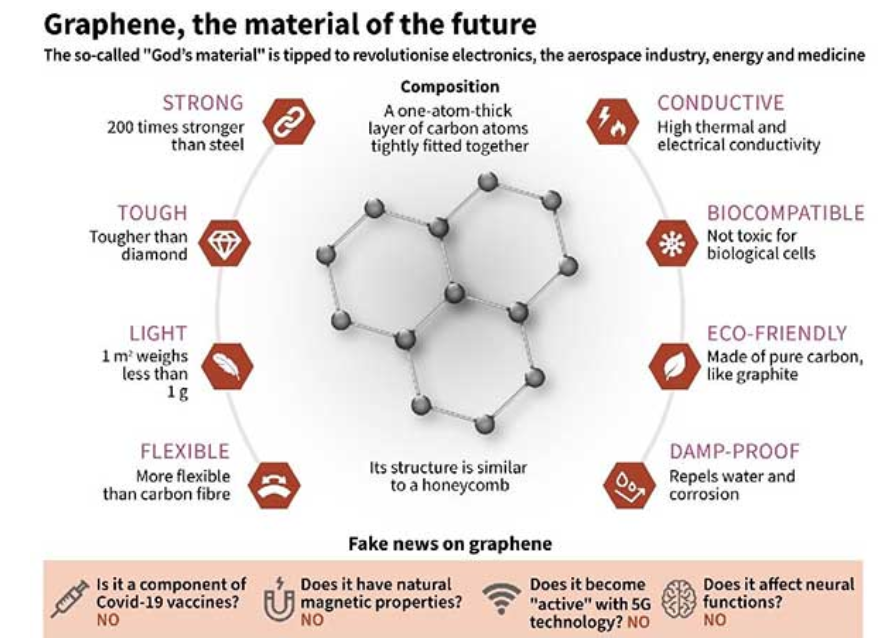
Graphene is a revolutionary material that has the potential to transform various industries such as electronics, energy, and healthcare. It is a thin layer of carbon atoms that are arranged in a hexagonal lattice pattern and is considered to be the strongest material known to man. In this blog post, we will discuss the basics of graphene for UPSC Prelims.
Properties of Graphene
Graphene has unique properties that make it an attractive material for various applications. It is an excellent conductor of electricity and has high thermal conductivity. It is also flexible, transparent, and has a large surface area. Due to its high surface area, graphene can be used for energy storage in batteries and supercapacitors. Its high strength and flexibility make it suitable for use in lightweight materials such as aircraft and sports equipment.
Technical Specifications of Graphene
- Thickness: One atom thick
- Density: 2.267 g/cm³
- Conductivity: 1,000 times greater than copper
- Strength: 200 times greater than steel
- Young’s modulus: 1 TPa (terapascal)
- Thermal conductivity: 5,000 W/mK (watts per meter Kelvin)
- Surface area: 2,630 m²/g (square meters per gram)

Applications of Graphene
Graphene has numerous applications in various industries. In the electronics industry, it can be used in transistors, touchscreens, and solar cells. Graphene-based transistors are faster and consume less power compared to traditional transistors. In the healthcare industry, it can be used in drug delivery and imaging. Graphene-based drug delivery systems can target specific cells and reduce side effects. In the energy industry, it can be used in batteries, supercapacitors, and solar cells. Graphene-based batteries and supercapacitors have higher energy density and faster charging times compared to traditional batteries.
Programs and Schemes in India Supporting Graphene
The Government of India has initiated several programs and schemes to encourage the usage of graphene. Some of the major programs and schemes are listed below:
- National Graphene Coordination Centre (NGCC): The NGCC has been established to promote research and development of graphene in India. It aims to create a platform for collaboration among researchers, academia, and industries.
- Nano Mission: The Nano Mission is a flagship program of the Government of India that aims to promote research and development in the field of nanotechnology. Graphene is one of the focus areas of this program.
- Department of Science and Technology (DST): The DST has initiated several programs to promote the usage of graphene in various industries. It has funded several research projects related to graphene.
- Graphene Entrepreneurship Park (GEP): The GEP is a joint initiative of the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras and the Tamil Nadu government. It aims to promote entrepreneurship in the field of graphene.
Challenges in Graphene Research
Despite its potential, there are several challenges in graphene research. One of the major challenges is the production of high-quality graphene in large quantities. Current production methods are expensive and time-consuming. Another challenge is the integration of graphene into existing technologies. The properties of graphene are different from traditional materials, and integrating it into existing technologies requires significant research and development.
Conclusion
Graphene is a revolutionary material that has the potential to transform various industries. Its unique properties make it an attractive material for various applications. The Government of India has initiated several programs and schemes to encourage the usage of graphene. However, there are several challenges in graphene research that need to be addressed. Aspirants appearing for UPSC Prelims should have a basic understanding of graphene and its applications, as well as the programs and schemes in India supporting graphene.
