Companion@360 → 7 Month programme to sharpen your writing skills → REGISTER NOW

What is La Nina effect ?
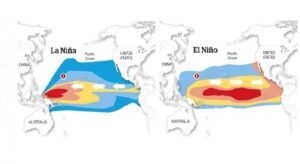
La Nina, the “cool phase” of ENSO, is a pattern that describes the unusual cooling of the tropical eastern Pacific. La Nina events may last between one and three years, unlike El Nino, which usually lasts no more than a year. Both phenomena tend to peak during the Northern Hemisphere winter.
La Nina means The Little Girl in Spanish. It is also sometimes called El Viejo, anti-El Nino, or simply “a cold event.”
La Nina events represent periods of below-average sea surface temperatures across the east-central Equatorial Pacific.
It is indicated by sea-surface temperature decreased by more than 0.9℉ for at least five successive three-month seasons.
The La Nina event is observed when the water temperature in the Eastern Pacific gets comparatively colder than normal, as a consequence of which, there is a strong high pressure over the eastern equatorial Pacific.
La Nina is caused by a build-up of cooler-than-normal waters in the tropical Pacific, the area of the Pacific Ocean between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
La Nina is characterized by lower-than-normal air pressure over the western Pacific. These low-pressure zones contribute to increased rainfall.
La Nina events are also associated with rainier-than-normal conditions over southeastern Africa and northern Brazil.
However, strong La Nina events are associated with catastrophic floods in northern Australia.
La Nina is also characterized by higher-than-normal pressure over the central and eastern Pacific.
This results in decreased cloud production and rainfall in that region.
Drier-than-normal conditions are observed along the west coast of tropical South America, the Gulf Coast of the United States, and the pampas region of southern South America.
La Nina influences the Indian subcontinent by piping in cold air from Siberia and South China, which interacts with the tropical heating to produce a north-south low-pressure system.
The cold air of La Nina associated with this north-south trough tends to extend much further south into India.
Read Also Teesta River