
India – US Relations
India-U.S. bilateral relations have developed into a “global strategic partnership”, based on shared democratic values, and growing convergence of interests on bilateral, regional, and global issues.
Regular exchange of high-level political visits, vibrant people-to-people interaction, and support across the political spectrum in both countries have nurtured and provided with sustained momentum in this bilateral relationship.
India-USA Relation – Background
During the cold war, India got tilted towards the Soviet Union after the 1971 Friendship Treaty, which was a response to the continuing U.S. tilt towards Pakistan and the beginnings of convergence between US and China
But in the post-cold war era, there has been a convergence in the interests of India and USA which can be attributed to several factors like – shift in global geopolitics in the post-Cold War era, India’s economic ascent, the rise of an assertive China, and India’s place on the global high table.
Thus, the relation between India and the US transformed from being Estranged democracies (during the cold war) to Strategic partners (in the post-cold war era).
Over the years, India-US relations have become increasingly multi-faceted, covering cooperation in areas such as trade, defense and security, education, science and technology, civil nuclear energy, space technology and applications, environment, and health.
Areas of Cooperation
- Shared ideals – The U.S-India partnership has its foundation in common values, including the rule of law and democratic principles, interests in promoting global security, stability, and economic prosperity through trade, investment, and connectivity.
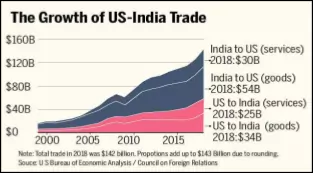
- Economic relations – US is India’s largest trading partner and inbound FDI from the US is more than $50 billion.
- In 2019, overall U.S.-India bilateral trade in goods and services reached $146.1 billion.
- Energy cooperation – US India launched a bilateral Strategic Energy Partnership in 2018 to enhance energy security, bolster strategic alignment, etc
- India has started importing Crude and LNG from US recently.
- Investment by Indian companies like Reliance, Essar and GAIL in the U.S. natural gas market is ushering in a new era of India-U.S. energy partnership.
- Nuclear Cooperation – India US Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement was signed in 2008.
- Signing of commercial agreement for Westinghouse (US Company) to build six nuclear reactors in Andhra Pradesh.
- High-Level Dialogue Mechanisms – India and the U.S. have more than 50 bilateral inter-governmental dialogue mechanisms for exchange of views on issues of mutual interest.
- 2+2 Annual Ministerial Dialogue is led by the Foreign and the Defence Ministers of India and then U.S. counterparts.
- Global Partnership – both are part of Quad grouping, and collaborate on forums like East Asia Summit, G-20
- U.S has expressed strong support for India’s candidature for a permanent seat/role in an expanded UN Security Council and for India’s early entry into the Nuclear Suppliers Group
- also, US expressed interest to India’s integration to G-7
- Defence Cooperation – Defence relationship has emerged as a major pillar of India-U.S. strategic partnership with the signing of ‘New Framework for India-U.S. Defence Relations’ in 2005.
- In 2014 US emerged as the top arms supplier to India by overtaking Russia. The U.S. categorized India as “a Major Defence Partner” in 2016
- US moved India up into Tier-I of “Strategic Trade Authorization” for unlicensed export of sensitive Defence items to India.
- India conducts more exercises with US forces than with any other country – Yudh Abhyas, Vajra Prahar, etc.
- India US has signed the 4 Defence Foundational agreements.

Strategic Convergence – Balancing China’s rise in the international system, and more particularly in the Indo-Pacific region, is a clear strategic convergence between India and the United States.
- The recently unveiled US Security Strategy recognizes India as a “leading global power” and “stronger strategic and defence partner” and seeks to increase quadrilateral cooperation with Japan, Australia, and India.
- Development of Indo-pacific – The US under its Pivot to Asia policy and Indo-Pacific Strategy views India as an ideal balancer to check the aggressive rise of China.
- Diaspora & people-to-people ties – Strength of Indian diaspora in US is around 4.5 million which is around 1% of its population.
- Indian Diaspora is acting as a catalyst to forge closer and stronger ties between India and the US.
- Collaboration in Science & Technology – a joint mission of ISRO and NASA is set to be launched in 2022, the world’s 1st dual-frequency Synthetic Aperture Radar satellite.
- A bilateral Joint Working Group on Civil Space Cooperation provides a forum for discussion on joint activities in space.
- Counter-Terrorism – India-U.S. Counter-Terrorism Cooperation Initiative was signed in 2010 to expand collaboration on counterterrorism, information sharing and capacity building
- US helped India in designating Jaish-e-Mohammad chief Masood Azhar as a global terrorist under UN Security Council Resolution 1267, and in placing Pakistan on grey-list of the Financial Action Task Force
- Cooperation in combating Covid-19 pandemic – India and the U.S have enhanced collaboration in R&D, especially in pharmaceuticals, therapeutics, and vaccine development
- Indian vaccine companies are collaborating with US based agencies to develop and produce a vaccine against COVID-19 on a rapid platform
Challenges in India-US Relationship
- Challenges in balancing India’s multi-faceted relationships with Iran and Russia
- India has been forced to stop concessional oil imports from Iran and Russia, and these heavy-handed American tactics have led to sharp rise in India’s oil import bill
- India-US interests clashed when India decided to the Russian made S-400 Triumph missile defense system despite threats of American sanctions
- US-Pakistan Relationship – Despite Washington’s claims to having de-hyphenated its relations with India and Pakistan, the US has not been able to extricate itself from the liabilities of its complex alliance with Pakistan.
- Trade Disputes – US recently removed India from its Generalized System of Preference (GSP) program, of which India was a huge beneficiary
- US levied tariffs on steel and aluminium products impacting Indian exports
- India has been referred by the US, as “tariff king” that imposes “tremendously high” import duties.
- WTO disputes – India USA are involved in WTO disputes on issues like, Capping prices of medical devices by India, greater Indian market access for American agriculture and dairy products etc.
- IPR conflicts – India is also on U.S.’s “Priority Watch List” which identifies countries posing challenges to American intellectual property rights.
- Currency manipulator tag for India – Recently, the United States added India to the ‘monitoring list’ of currency manipulating countries.
- Internal Issues in India – criticism from the US Congress and some parts of US civil society is pushing the US administration to tell India to bring Kashmir to normalcy and not go ahead with the new citizenship law followed by the NRC
- 2020 Human Rights Report by US State Department – mentions India has several human rights issues such as restrictions on freedom of expression and the press, Crimes involving violence and discrimination targeting members of minority groups, etc.
- India as a Country of Particular concern – The US Commission on International Religious Freedom recommended classifying India as a Country of Particular Concern (CPC)
- it also recommended targeted sanctions on Indian individuals and entities for ‘severe violations of religious freedom’
- The US conducted a Freedom of Navigation operation (FONOP) in India’s Exclusive Economic Zone without taking permission from New Delhi.
Converting Concerns into Opportunities
- Job Creation through Trade and Exports – with the Biden administration setting an ambitious target for US-India trade and businesses in both countries looking for diversifying their manufacturing supply chains, there is huge potential for the creation of employment in manufacturing.
- An area where strategic considerations and imperatives of job creation converge is defence, especially since India has been designated a Major Defence Partner of the US.
- Cooperation in Healthcare – The two countries can also work with multilateral agencies across the spectrum of vaccine (including Covid vaccine) development, logistics and distribution.
- India can benefit from advancements in medical technologies, devices, new medicines and R&D capabilities
- Indian pharma sector can play a role in reducing health costs of American consumers by developing generic medicines.
- Focus on Infrastructure – provides huge investment opportunities for US companies in India in transportation, power, urban amenities, and renewable energy technologies.
- This could boost India’s infrastructure development.
- Enhance opportunities in 5G Tech – Increased partnership between the two nations can accelerate the development of technology solutions, promote vendors in the 5G open ecosystem and drive economic growth.
- The two countries should engage in shaping the rules of a new order in this space.
- Multilateralism for cooperation in wider areas – with the ascendancy of the Indo-Pacific paradigm and platforms like Quad, Quad-Plus, India could widen cooperation beyond defence and security, including economics, technology and developments pertaining to the regional order.
- Strengthening Civil Nuclear cooperation – Civil Nuclear Cooperation has not taken off despite the historic nuclear deal of 2008 because of the nuclear liability law in India and Westinghouse’s bankruptcy.
- Reviving this conversation could help meet India’s energy needs.
The US appears to have a positive vision of strategic convergence between India and the US and fully appreciates the need for two countries to work together not only for mutual benefit but also for the sake of global peace.
Way Forward
India, on its way to become a global power, will likely have to follow a zigzag course, balancing between American demands, long-term friendship with Russia and its own strategic necessities in the neighbourhood and beyond
While India can play a crucial role in America’s Indo-Pacific strategy, the US can help India stand up to China’s assertiveness
Both countries should take steps to improve their bilateral relations such as expanding dialogue on emerging threats in the Cyber and Space domains, and broader collaboration between defence industries
India should utilize the strong people-to-people ties of the Indian diaspora to claim relaxations from US sanctions under CAATSA provisions, for S-400 missile purchase from Russia, and oil purchase from Iran
While US need to be more sensitive towards India’s reservations against its soft policy towards Pakistan, India needs to prepare itself for a larger security role in Afghanistan in a big way.
Both countries should take proactive steps towards stable foreign policy development.
India-US relation remains critical for the shaping of world order in the 21st century. In order to realise the full potential of relations, the two governments must now strive to complete the unfinished agreements and set the course for a stronger Comprehensive Strategic Global Partnership.
Previous Year Questions
- In what ways would the ongoing US-Iran Nuclear Pact Controversy affect the national interest of India? How should India respond to its situation? (2018)
- What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s national self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. (2019)
- What is the significance of Indo-US deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (2020)
Enroll today with the best civils service academy and take your first step towards your Civils journey.
Feel free to reach out to us for any inquiries, collaborations, or support. We’re here to help.


