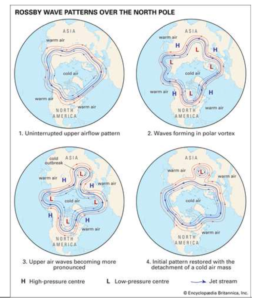
Rossby waves
Rossby waves are formed when polar air moves toward the Equator while tropical air is moving poleward. Because of the temperature difference between the Equator and the poles due to differences in the amounts of solar radiation received, heat tends to flow from low to high latitudes; this is accomplished, in part, by these air movements.
- Rossby waves are a dominant component of the Ferrel circulation. The tropical air carries heat poleward, and the polar air absorbs heat as it moves toward the Equator.
- The existence of these waves explains the low-pressure cells (cyclones) and high-pressure cells (anticyclones) that are important in producing the weather of the middle and higher latitudes.
Jet streams:
- Jet streams are wind streams that reach great speeds in narrow zones at a high altitude.
- They occur where atmospheric pressure gradients are strong.
- The greatest wind speeds occur in the center of the jet stream, with velocities decreasing away from it.
- Each hemisphere normally exhibits westerly polar and subtropical jet streams.
- An easterly jet occurs in summer over Asia and Africa.
Read Also Nanomicelles
Oceanic Rossby Waves:
- Waves in the ocean come in many different shapes and sizes. Slow-moving oceanic Rossby waves are fundamentally different from ocean surface waves.
- Unlike waves that break along the shore, Rossby waves are huge, undulating movements of the ocean that stretch horizontally across the planet for hundreds of kilometers in a westward direction.
- They are so large and massive that they can change Earth’s climate conditions.
- Along with rising sea levels, King Tides, and the effects of El Niño, oceanic Rossby waves contribute to high tides and coastal flooding in some regions of the world.
- Rossby wave movement is complex. The horizontal wave speed of a Rossby (the amount of time it takes the wave to travel across an ocean basin) is dependent upon the latitude of the wave.
- In the Pacific, for instance, waves at lower latitudes (closer to the equator) may take months to a year to cross the ocean.
- Waves that form farther away from the equator (at mid-latitudes) of the Pacific may take closer to 10 to 20 years to make the journey.
- The vertical motion of Rossby waves is small along the ocean’s surface and large along the deeper thermocline — the transition area between the ocean’s warm upper layer and colder depths.
- This variation in vertical motion of the water’s surface can be quite dramatic: the typical vertical movement of the water’s surface is generally four inches or less, while the vertical movement of the thermocline for the same wave is approximately 1,000 times greater.
- In other words, for a four inch or less surface displacement along the ocean surface, there may be more than 300 feet of corresponding vertical movement in the thermocline far below the surface.
- Due to the small vertical movement along the ocean surface, oceanic Rossby waves are undetectable by the human eye. Scientists typically rely on satellite radar altimetry to detect the massive waves.
Atmospheric Rossby Waves:
- According to the National Weather Service, atmospheric Rossby waves form primarily as a result of the Earth’s geography.
- Rossby waves help transfer heat from the tropics toward the poles and cold air toward the tropics in an attempt to return atmosphere to balance.
- They also help locate the jet stream and mark out the track of surface low pressure systems.
- The slow motion of these waves often results in fairly long, persistent weather patterns.