New Development Bank
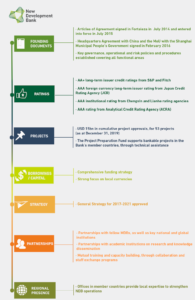
- At the fourth BRICS Summit in New Delhi (2012), the leaders of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa considered the possibility of setting up a new Development Bank to mobilize resources for infrastructure and sustainable development projects in BRICS and other emerging economies, as well as in developing countries.
- During the sixth BRICS Summit in Fortaleza (2014), the leaders signed the Agreement establishing the New Development Bank (NDB).
Significance of New Development Bank
- The daily passenger traffic along the Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut corridor of the National Capital Region is 0.69 million. Of this, around 63% use private vehicles.
- Due to traffic congestion, the time taken to transit between Delhi and Meerut is about 3 to 4 hours.
- Also, the traffic congestion in the route is adding to the air pollution in the NCR region. Thus, it is essential to implement the Rapid Transit System Project.
- India asked the New Development Bank (NDB) to enhance the emergency facilities to $10 billion to deal with the challenges posed by the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The country appreciated the efforts of the multilateral lending agency on fast-tracking of financial assistance of about $5 billion to BRICS countries, including emergency assistance of $1 billion to India to combat the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Lauding efforts of the NDB in establishing itself as a credible Global Financial Institution, India said it should take appropriate actions to join G-20 forum along with other Multilateral Development Bank (MDBs)/ International Financial Institutions (IFIs).
Objectives:
- Fostering the development of member countries.
- Supporting economic growth.
- Promoting competitiveness and facilitating job creation.
- Building a knowledge-sharing platform among developing countries.
- Multi theme.
- Clean energy
- Social Infrastructure
- Environmental efficiency
- Urban development
- Irrigation, water resources and sanitation management
- Transport infrastructure
Regional rapid transit system:
- The Regional Rapid Transit System connects the fastest-developing small towns in the National Capital Region.
- The main objective of the project is to reduce the dependence on Roadways. It is being implemented by the National Capital Region Transport Corporation.
Initiatives taken:
- Announcement of a scheme of social support measures amounting to $25 billion (Rs 1.70 lakh crore) to alleviate the hardship of the poor and the vulnerable.
- Insurance cover of $67,000 (Rs 50 lakh) per person to over 2.2 million frontline health workers and others provision of relief to firms in statutory and regulatory compliance matters.
- Creating a COVID-19 Emergency Fund
- Allocation of $2 billion (Rs 15,000 crore) by the government for strengthening the healthcare system.

- To fulfill its purpose, the Bank supports public or private projects through loans, guarantees, equity participation and other financial instruments
- The NDB is building a robust and diversified portfolio of sustainable infrastructure projects, in order to fulfill its mandate and achieve strategic objectives.