
Cyber security and Cyber Crime
Cybersecurity spends in India is rising rapidly because of the massive digitization movement, especially in payments, and the case of internet use on mobile. Cybersecurity means securing cyberspace from attack and economic espionage.
Cybersecurity Cyber Space:
Cyber Space is interconnected of IT infrastructure such as the Internet, Telecom network, Computer systems, etc.
- In 3rd Global Security Index released by the ITU,India slipped to 47th rank in 2018 from 23rd in 2017.
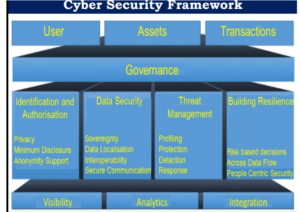
Cybersecurity framework
Cyber Crime:
- Gambling:In India are entitled to formulate laws for gambling activities.
- Illegal articles: Sales of illegal articles such as narcotics drugs, weapons, wildlife,etc..is being facilitated by the internet.
- Email Spamming: Unsolicited message sent in bulk by email.
- Cyber Warfare:India was one of the most cyber-targeted countries in the world in 2019 with over 50,000 cyber- attacks from china alone.
- Digital Forejery: The process of manipulating documents or images for the intent of financial, social or political gain.
- Cyber Defamation:It is an act of intentionally insulting, defaming or offending another individual or a party through a virtual medium.
Need for Cyber Security:
- Prevent Economic loss: The estimated cost of cyber-attacks in India stands at $4 billion which is expected to reach $20 billion in the next 10 years.
- Increasing Internet users: India ranks 3rd in terms of the highest number of
internet users in the world after the USA and China, the
the number has grown 6-fold between 2012-2017 with a
the compound annual growth rate of 44%. - Cyber Terrorism: The use of the Internet to conduct violent acts that result in, or threaten, loss of life or significant bodily harm, in order to achieve political or ideological gains through threat or intimidation.
- Government Digital Push: Various Programs of government such as Bharat Net, Aadhaar, MyGov, etc Are prompting a large number of citizens, companies Government agencies to transact online.
- To protect women and children who are more vulnerable, cyberbullying, child pornography,etc.
Challenges to Cyber Security:
- Digital illiteracy: It makes Indian citizens highly susceptible to cyber fraud, cyber theft, etc..
- Lack of adoption of new technology:
- Anonymity:
- Lack of coordination among various agencies:
- Increased cyberspace by terrorists.
- Cyberspace has inherent vulnerabilities that cannot be removed
- The proliferation of the internet of things(IoT)and lack of proper security infrastructure in some devices

Tools to Protect Against Cyber Threats:
- Digital signature: Digital signatures are like electronic “fingerprints.” In the form of a coded message, the digital signature securely associates a signer with a document in a recorded transaction.
- Encryption: Encryption is a process that encodes a message or file so that it can be only be read by certain people
- Cyberforensics: is a branch of digital forensic science pertaining to evidence found in computers and digital storage media.
- Security audit: A security audit is a systematic evaluation of the security of a company’s information system by measuring how well it conforms to a set of established criteria.
- Traditional tool: Importance of use of antivirus, strong passwords, secure Wi-fi connection,etc..need to emphasized.
National cybersecurity policy,2013:
- To protect information and information infrastructure in cyberspace, build capabilities to prevent and respond to cyber threats, reduce vulnerabilities and minimize damage from cyber incidents through a combination of institutional structures, people, processes, technology and cooperation.
- To build a secure and resilient cyberspace for citizens, businesses and Government.
Recent Steps were taken by Government:
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: In 2017, this platform was introduced for internet users to clean their computers and devices by wiping out viruses and malware.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs is implementing Cyber Crime Prevention against Women and Children scheme.
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre(NCIIPC)to Battle cybersecurity threats in the strategic area such as air control,nuclear and space.
- National Cybersecurity Coordination Centre (NCCC): In 2017, the NCCC was developed. Its mandate is to scan internet traffic and communication metadata (which are little snippets of information hidden inside each communication) coming into the country to detect real-time cyber threats.
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative: It was launched in 2018 with an aim to spread awareness about cybercrime and building capacity for safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
Way forward
- The proposed project NETRA for internet surveillance should be taken up. Concerns about privacy and freedom of expression have to be taken care of.
National Cyber Security Policy should be amended according to the changing times and need.
- State Governments should also be taken up operations for Cybersecurity.
FOR Example SHE Team of Telangana Government has been successful in protecting women from online harassment and cybercrimes. Similar initiatives could be taken up by other states as well.
Enroll today with the best civils service academy and take your first step towards your Civils journey.
Feel free to reach out to us for any inquiries, collaborations, or support. We’re here to help.

